Working with LLMs in Ruby on Rails: A Simple Guide
Why You Need to Work with LLMs Today #
Large Language Models (LLMs) are reshaping how we build apps. Knowing how to use LLMs lets you create smart, interactive tools that understand and generate text. This skill is now key in modern development. Whether you build chatbots or text analyzers, LLMs can add value. So, let’s dive into how to run an LLM server locally and use it in a Ruby on Rails (RoR) project.
Running LLM Locally with Docker #
We will run the Llama 3.1 model using Docker. Llama 3.1 is popular for personal use, and Docker simplifies the setup.
Install Docker: Use the official Docker client with a UI.
Run the LLM Server: Use the following command to start the Llama 3.1 with API server
docker run -d -v ollama:/root/.ollama -p 11434:11434 --name ollama ollama/ollamaSelect LLM model:
docker exec -it ollama ollama run llama3Test the server with:
curl http://localhost:11434/api/generate -d '{"model": "llama3", "prompt":"Why is the sky blue? Answer with 10 words"}'
If the result looks something like this, then the server has started successfully:
{"model":"llama3","created_at":"2024-08-28T15:01:07.826076294Z","response":"Short","done":false}
{"model":"llama3","created_at":"2024-08-28T15:01:08.154276586Z","response":" wavelength","done":false}
{"model":"llama3","created_at":"2024-08-28T15:01:08.314917461Z","response":" blue","done":false}
{"model":"llama3","created_at":"2024-08-28T15:01:08.490800211Z","response":" light","done":false}
{"model":"llama3","created_at":"2024-08-28T15:01:08.661478628Z","response":" sc","done":false}
{"model":"llama3","created_at":"2024-08-28T15:01:08.83101417Z","response":"atters","done":false}
{"model":"llama3","created_at":"2024-08-28T15:01:09.002102128Z","response":" more","done":false}
{"model":"llama3","created_at":"2024-08-28T15:01:09.175030712Z","response":" in","done":false}
{"model":"llama3","created_at":"2024-08-28T15:01:09.34067667Z","response":" Earth","done":false}
{"model":"llama3","created_at":"2024-08-28T15:01:09.512882962Z","response":"'s","done":false}
{"model":"llama3","created_at":"2024-08-28T15:01:09.685311962Z","response":" atmosphere","done":false}
{"model":"llama3","created_at":"2024-08-28T15:01:09.87469392Z","response":".","done":false}
{"model":"llama3","created_at":"2024-08-28T15:01:10.089219045Z","response":"","done":true,"done_reason":"stop","context":[128006,882,128007,271,10445,374,279,13180,6437,30,22559,449,220,605,4339,128009,128006,78191,128007,271,12755,46406,6437,3177,1156,10385,810,304,9420,596,16975,13],"total_duration":12195522088,"load_duration":7132571086,"prompt_eval_count":21,"prompt_eval_duration":2754452000,"eval_count":13,"eval_duration":2263609000}
Llama server API documentation .
Building a Ruby on Rails App #
Let’s create a simple RoR app that connects to our LLM server.
- Create a New Ruby on Rails Project:
rails new llm-chat
- Generate a Controller with actions:
rails g controller chat index create
- Add a Routes for Chat: In config/routes.rb, add:
root "chat#index"
post "/", to: "chat#create", controller: :chat
- Add WebSocket Route: In config/routes.rb, add:
mount ActionCable.server => '/cable'
- Generate a WebSocket Channel:
rails generate channel Chat
- Update the Chat Channel: In
app/channels/chat_channel.rb, update the code:
class ChatChannel < ApplicationCable::Channel
def subscribed
stream_from "chat_channel"
end
def unsubscribed
end
end
- Update the Controller: In
app/controllers/chat_controller.rb, modify the create method:
class ChatController < ApplicationController
def index; end
def create
LlmJob.perform_later("http://localhost:11434/api/generate", params[:chat][:query])
head :ok
end
end
- Create LlmJob:
╰─ $ rails generate job Llm
invoke test_unit
create test/jobs/llm_job_test.rb
create app/jobs/llm_job.rb
- LlmJob code:
require 'net/http'
class LlmJob < ApplicationJob
queue_as :default
def perform(api_endpoint, prompt)
uri = URI(api_endpoint)
req = Net::HTTP::Post.new(uri, 'Content-Type' => 'application/json')
req.body = { model: "llama3", prompt: prompt }.to_json
Net::HTTP.start(uri.hostname, uri.port) do |http|
http.request(req) do |response|
response.read_body do |chunk|
parsed_response = JSON.parse(chunk)
ActionCable.server.broadcast(
"chat_channel",
{ message: parsed_response['response'], done: parsed_response['done'] }
)
end
end
end
end
end
- Frontend Chat Channel: In app/javascript/channels/chat_channel.js, add:
import { createConsumer } from "@rails/actioncable"
const consumer = createConsumer()
consumer.subscriptions.create("ChatChannel", {
received(data) {
document.getElementById("send-request").disabled = true;
const chatBox = document.getElementById('chat-box');
let botMessageElement = chatBox.querySelector('div[data-status="pending"]');
if (!botMessageElement) {
botMessageElement = document.createElement('div');
botMessageElement.className = 'message bot';
botMessageElement.setAttribute('data-status', 'pending');
chatBox.appendChild(botMessageElement);
}
botMessageElement.textContent += ` ${data.message}`;
if (data.done) {
botMessageElement.setAttribute('data-status', 'done');
document.getElementById("send-request").disabled = false;
}
chatBox.scrollTop = chatBox.scrollHeight;
}
});
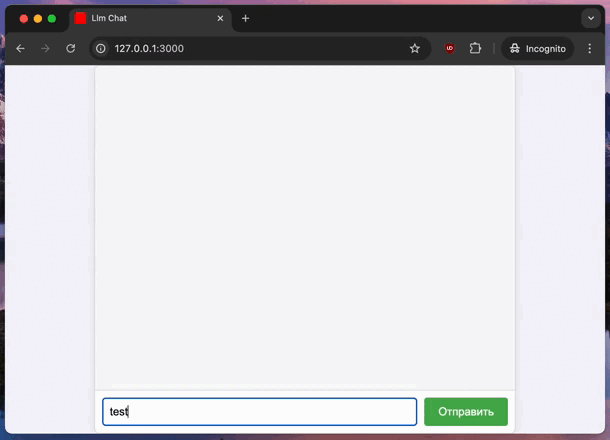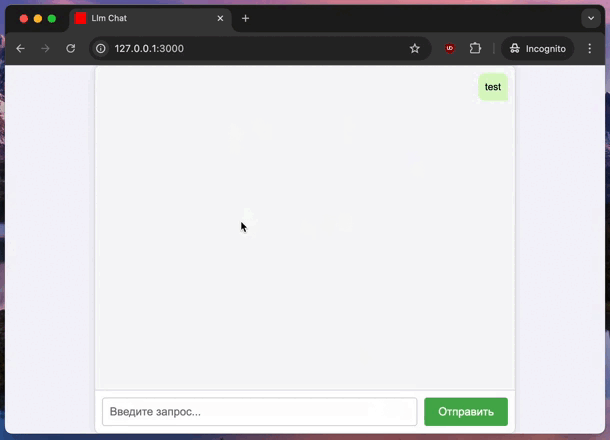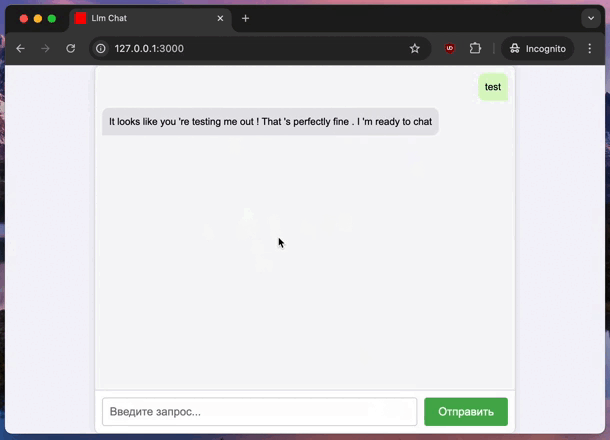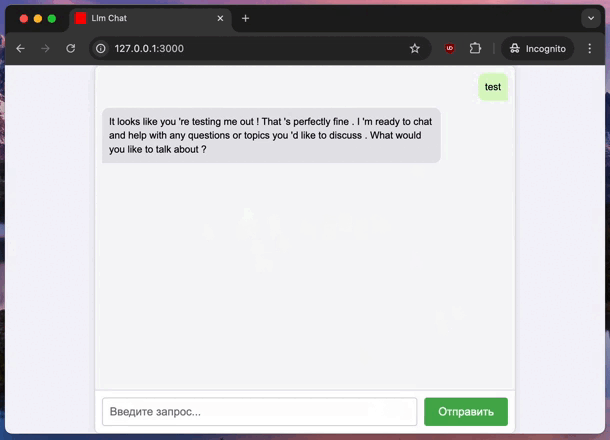
Conclusion #
Now, you have a basic RoR app that interacts with an LLM server. The server sends responses in chunks, and the app displays them in real-time. This setup is a powerful way to integrate AI into your apps.
Full code you can find here: Github repo