How To Setup Default Values For Attributes In Ruby On Rails
Have you ever thought setting default values for attributes in Ruby on Rails could be problematic?
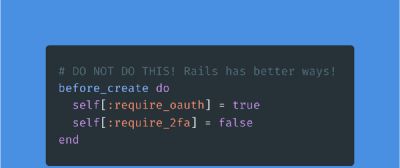
Since attributes are uninitialized when a new model is created without any parameters, default values will be set according to the attribute type.
This idea is perfect if we don’t want to fill the database with unnecessary information.
Ruby on Rails provides many options for adding default values, but not all of them are good.
Here is a list of good examples of how you should add default values:
- Option 1: Set the default value directly in the database via migrations.
- Option 2: Use
after_initializecallback. - Option 3: Use
before_validatecallback. Set the default value in the model, but only if it is nil.
Option 1: Set the default value directly in the database via migrations #
In Ruby on Rails, you can set default values for database attributes by including them in your migration.
The syntax is default: 'value'.
This is useful if you want to define many attributes at once. When looking at your db/schema.rb file, it’s easy to see the default value at a glance.
class CreateUsers < ActiveRecord::Migration
def change
create_table :users do |t|
t.string :name, default: "First Last", null: false
end
end
end
Option 2: Use after_initialize callback #
There is after_initialize callback to help a developer to set default values,
especially if they are required to do some computation.
This callback is invoked after initiating the model so the developer can access default values before updating it.
For example, let’s say we want to set a default name for our user in our app:
class User < ApplicationRecord
after_initialize :set_defaults
def set_defaults
name = "First Last"
end
end
Option 3: Use before_validate callback. Set the default value in the model when it is missed #
In Ruby on Rails, you can use before_validation to set default values for model attributes.
This is a great way to ensure that your models always have valid attributes, and it’s elementary to do:
class User < ApplicationRecord
before_validation :set_defaults
private
def set_defaults
name = "First Last" if name.blank?
end
end
Option 4: Through Rails Attributes API #
And last most ideal way is to use Rails Attributes API
. You can add default value in the model like attribute :my_string, :string, default: "new default"
# db/schema.rb
create_table :store_listings, force: true do |t|
t.string :my_string, default: "original default"
end
StoreListing.new.my_string # => "original default"
# app/models/store_listing.rb
class StoreListing < ActiveRecord::Base
attribute :my_string, :string, default: "new default"
end
StoreListing.new.my_string # => "new default"
class Product < ActiveRecord::Base
attribute :my_default_proc, :datetime, default: -> { Time.now }
end
Product.new.my_default_proc # => 2015-05-30 11:04:48 -0600
sleep 1
Product.new.my_default_proc # => 2015-05-30 11:04:49 -0600
And that’s it!
It is worth mentioning #
- Do not override with default values original changes, which breaks the ActiveRecord contract:
def set_defaults
name = "First Last"
end
(This unexpected behavior will confuse developers)
- Do not set defaults after validations. Prefer to add default values only before validation to make sure that we support consistency
before_save :set_defaults
private
def set_defaults
name = nil if name.blank?
end
(This will add invalid data in the DB or raise Runtime Error)